|
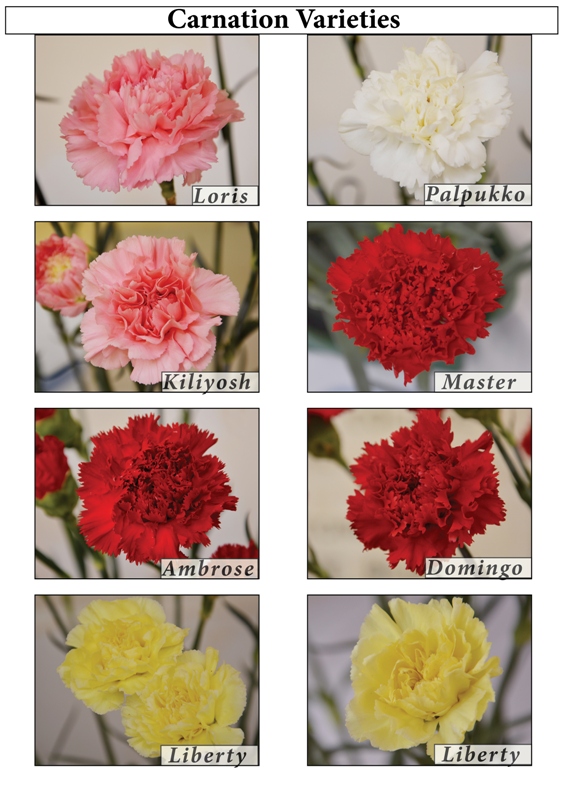
Varieties
Standard Types
Red- Domingo, Master, Gaudina, Leopardii, Big Red, Taureg, Guapo, Aicardii
White- Baltico, White Liberty, Emotion, White Dona, Lisa
Pink- Dona, Charmant, Dumas, Pink Dover, Bizet
Light pink - Charmant, Cipro Big Mama, Dona, Golem
Yellow - Diana, Kiro, Soto, Salamanca, Liberty
Orange - Solar, Star, Folgore
Double - Malaga, Star, Athena, Happy Golem

|
|

|
PINK DONA |
TUNDRA |
WHITE TUNDRA |
Spray Types
Estimade, Indira, Vera, Durago, Amore, Kiss Siga are some of the popular spray types.
Red- Red Eye, Red Fuego, Red Vital, Aveiro
White- White Prestige, Milky Way, Elvis,T-587
Pink- Rosa Bebe, Spur, Suprema, D- 925, Celebration, Osiris
Yellow - Stella, Prestige, Mila, Sonia, Abril
Orange - Sunshine, Autumn, Fancy Fuego, Disney, Eilat
Double - Berry, Orbit Plus, Nadeja, Picaro |

Spray types |
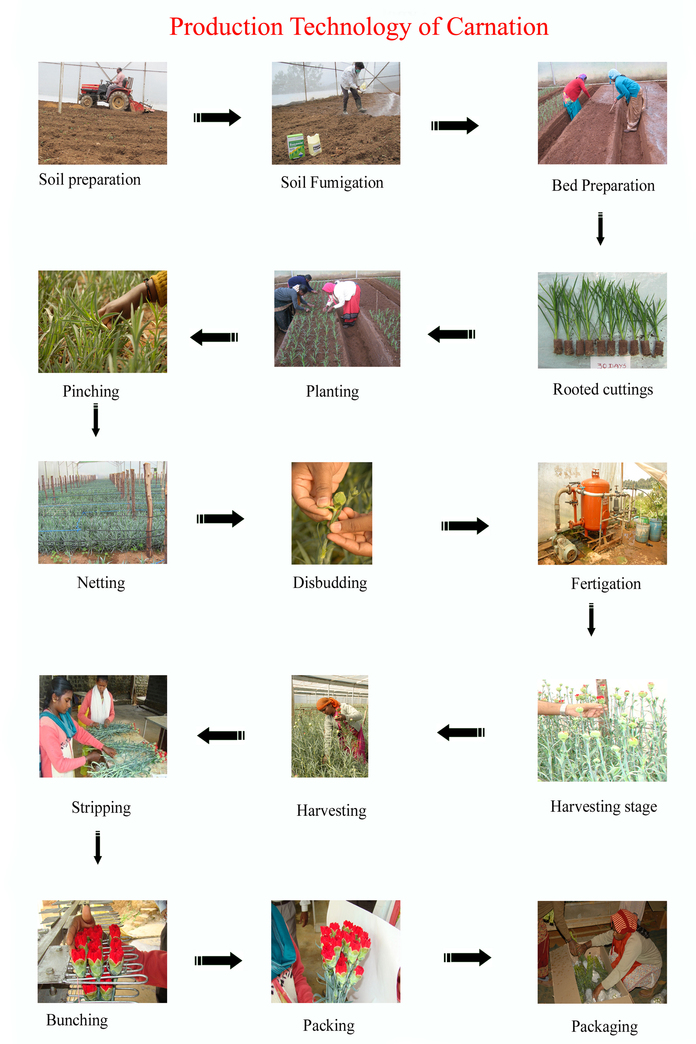 |
Growing environment: Naturally ventilated aerodynamic steel frame structure.
Climate: Cool climate with day temperature of 18-240C and night temperature of 10-150C; relative humidity of 70 -75 %.
Soil: Well drained red loamy soil with pH of 5.5 - 6.5.
Season
It can be cultivated throughout the year as it is grown under controlled conditions.
Propagation and Planting
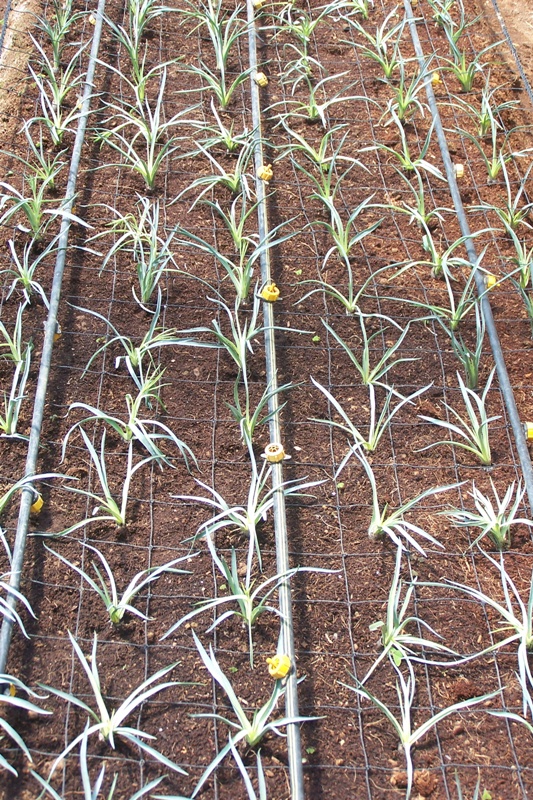
Plantlets/suckers can be used for planting. The terminal cuttings of 5-10 cm are treated with NAA at 500 ppm for 5 minutes to induce rooting. Cuttings are dipped in Carbendazim 2g/lit solution. Raised beds at 3 feet width and 45 cm height are formed at 45 cm interval and planting is done on top of the bed at 15 x 15 cm spacing. The cuttings normally develop good root system within 21 days.
Fumigation - Dazomet @ 30g/m2 or H2O2 @ 300 ml/m2.
Bed size:100 cm width, 30 cm height, convenient length with 40 cm foot path.
Spacing: 6 row planting - 15x15 cm (25 plants/m2).
4 row planting - 15x15cm (22 plants/m2) .
Irrigation: Drip system with drippers at 30 cm spacing (5-6 l/m2/day).
Growing condition – Day temperature 20-25oC
Night temperature 10-15oC
Critical photoperiod 13 hours
RH 50-60%
|
|
| Planting method in carnation |
 |
 |
 |
Nutrition:
The following fertigation schedule can be adopted for intensive production under polyhouse conditions.
| Nutrients |
Quantity (g/m2/week) |
| Till bud formation |
Bud formation to harvest |
| Tank-A (Monday and Thursday) |
| Ammonium Nitrate |
3.0 g |
2.0 g |
| 19:19:19 |
3.0 g |
2.0 g |
| Magnesium Sulphate |
2.5 g |
2.5 g |
| Boron |
1.0 g |
1.0 g |
| Trace elements / micronutrients |
1.0 g |
1.0 g |
| Tank – B (Tuesday and Friday) |
| Potassium Nitrate |
5.0 g |
5.0 g |
| Calcium Nitrate |
8.0 g |
9.0 g |
Special practices
Netting for plant support: 4 layers
1st layer : 7.5 x 7.5 cm
2nd layer : 10 x 10 cm
3 rd layer : 12.5 x 12.5 cm
4 th layer : 15 x 15 cm
 |
 |
| Netting practice in carnation |
Support Material
Carnation crop has the tendency to bend unless supported properly. Hence the crop needs support while growing. Good support material is metallic wire woven with nylon mesh. At every two meters the wire should be supported with poles. The poles at both the ends of bed should be strong. Metallic wire is tied around the bed along the length with the support from supporting poles. Across the bed, nylon wires are woven like net. For an optimum support, an increasing width of the meshes can be used. Bottom net can be of 10x10cm, then two nets of 12.5x12.5cm and the upper most can be 15x15cm.
Pinching
- Depending upon the need of crop spread, single, one and a half or double pinch method is adopted.
- Ideal time for pinching is early morning.
- When the plant attains 5 nodes, the first pinch is given. This is called ‘single pinch’. This would give rise to six lateral shoots.
- With a ‘one and half pinch’, 2-3 of these lateral shoots are pinched again. For the ‘double pinch’, all the lateral shoots are pinched off.

Pinching in Carnation
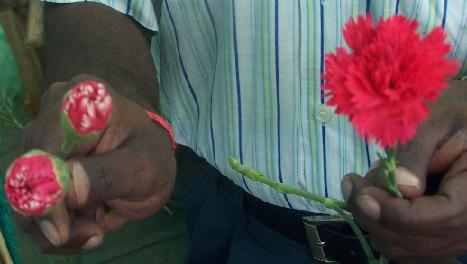
Disbudding
In standard carnations, side buds should be removed whereas in spray carnations, the terminal bud has to be removed.
Irrigation
Irrigation is provided with drip system once in 2-3 days according to soil moisture to maintain water holding capacity at 60% to 65%. The optimum water requirement of the crop is 4-5 lit/m2/day
Manuring
Neem cake 2.5 ton/ha, Phosphorus 400 g/100 sq.feet and Magnesium sulphate 0.5 kg/100 sq.feet are applied as basal. Top dressing
Calcium Ammonium Nitrate and MOP at 5:3 ratio is mixed and applied @ 2.5 g/plant/month as top dressing.
| Field overview in different stages of crop |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Plant Protection
|
Aphids - Myzus persicae
Damage symptom
Feeding usually occurs in buds and undersides of leaves. Feeding on young leaves results in distorted leaves as they continue to grow. Older leaves may display patches of chlorolic spots. Nymphs and adults suck the sap from the leaves, stems and flower buds in colonies.
Control
Spraying the plants with Thiomethoxam 1ml/litre or Imidachloprid @ 2ml/litre or Asatap (Acephate) @ 0.5 to 1.0 gm/litre.
|
 |
Thrips: Thrips tabaci
Damage symptom
Both the nymphs and adults suck the sap from leaves and flower. They excrete brown droplets, which afterwards true black. Leaves may fade and shrivel in case of heavy infestation and foliage becomes silvery.
Control measures
Spraying of Fipronil 1.5 ml/lit (or) Imidachloprid 2ml/litre or Dimethoate 30 EC @ 1ml/litre.
 |
 |
| Thrips infested |
Normal |
Red spider mites-Tetranychus urticae
Damage symptom
These have ability to produce fine silk webbing, spider mites are very tiny and very small and are difficult to identify. They suck sap from the leaves which results in tiny yellow or white speckles. Once the foliage of a plant becomes bronze it often drops prematurely. Heavily infested plant may be discoloured stunted.
 |
 |
 |
| Red spider mite |
Infested bud |
Ballooning symptom |
Control
- Apply Abamectin (Vermitec) 1.9EC @ 0.5ml/litre
- Spray Azardiractin 50,000ppm 3ml/litre
- Discard the plant and leaf debris.
Bud borer – Helicoverpa armigera
Caterpillers infest the leaves and flower buds. Bore holes are clearly visible on flower buds. Finally the infested flower buds are fail to open. The attack by this pest is most during warm season.
Control
- Spray Bacillus thuringiensis 2g/litre.
- Release 1 lakhs of Trichogramma egg parasitoid per acre.
- Set up Helilure sex pheromone trap @ 4 Nos/acre
- Spray spinosad 0.75ml/litre or Thiodicarp 0.5 ml/litre
Diseases
Fusarium wilt: Soil drenching with Carbendazim @ 0.1 % or Difenoconazole @ 0.05 %orPseudomonas fluorescens as soil application @ 25 g/m2 and foliar application @ 0.5 % at monthly intervals orsoil drenching with Bacillus amyloliquefaciens @ 0.5 % at monthly intervals |
Alternarialeaf spot: Bacillus subtilis as soil application @ 25 g/m2 followed by foliar application @ 0.5 % at monthly intervals
Physiological disorder
Calyx splitting: Spray borax @ 1 g/l at fortnightly intervals till flower bud appearance and at weekly intervals thereafter.
Harvest: Flowering starts 110-120 days after planting.
Stages of harvest
Standard types - paint brush stage
Spray types - when two flowers are open and the remaining flower buds show colour
Yield: 15 flowers/plant (350 - 375 flowers stems/m2) in 2 years period.
Fusarium wilt
Grey Mould rot
Disorder
Calyx Splitting
Cultivars with too many petals are susceptible to calyx splitting. Varying temperature and environmental conditions also influences calyx splitting. The calyx may split down either half or completely. The petals are deprived of their support, which results in bending down of petals. Thus, the regularity of shape and structure of the flower get destroyed. Selection of cultivars like Epson, Palmir etc. that are less prone to splitting, regulation of temperature and maintenance of optimal fertilizer level can minimize this disorder. This can also be reduced by placing a rubber band or 6mm wide clear plastic tape is used around the calyx of the flowers which are just start opening.
Curly tip
This disorder affects the growing tips which curl and become distorted. Tips of the young shoots fail to separate and continuation of growth results in a characteristic curvature. Poor light and other adverse conditions are thought to be the causes of the disorder. Water stress and potassium deficiency are suspected causes for a physiological curly tip and die-back of carnation flowers.
Season of Flowering development and Harvest
Flower starts after 4 months of planting and continues up to one and half years. Standard carnation flowers are harvested when the outer petals unfold nearly perpendicular to the stem. Spray types are harvested when two flowers open and the remaining buds show colour. Daily harvest is made leaving bottom 5 nodes of stalk to facilitate side shoot development.
Post harvest Treatment
Citric acid is added to water to make the pH 4.5 to 5 and 5 mg of Sodium hypochloride is added to 1 litre of water. Cut flower stalk is soaked in this solution for 4 – 5 hours to improve vase life.
After harvest, the flower stems have to be trimmed at the base and should be immediately placed in a bucket of preservative solution of warm and deionized water. A good preservative solution for carnations should be acidic (pH 4.5) with 2-5% sucrose and a biocide not phytotoxic to carnations. After keeping in preservative solution for 2 to 4 hours, flowers should be placed in a refrigerated room at 0-2°C for 12-24 hours. The flowers can be stored for two to four weeks before marketing. For this, the flowers have to be packed in cartons lined with polyethylene film. These cartons should have sufficient vent holes. The full cartons should be pre-cooled with out lid. The plastic is then loosely folded on top of the stems and the lid is closed. These cartons are stored in cool chambers designed to maintained 0°C with good air circulation and a constant relative humidity of 90-95%.
Grading
Based on stem thickness, stem length and quality of flower grading is done as A, B, C, D.
Yield
The average yield is about 8 Stalks/plant/year

Grading and packing in carnation
*Precision production techniques for carnation
| S.No. |
Cultural Practice |
Recommendation |
| 1. |
Fumigation |
Dazomet @ 30 g/m2 |
| 2. |
Media consortium |
10:1:1 ratio of 30 kg/m2of consortium with 25 kg of Farm Yard Manure, 2.5 kg of vermicompost, 2.5 kg of cocopeat with the biofertilizers Azospirillum, Phosphobacteria, VAM and the biocontrol agents Trichoderma viridae, Pseudomonas fluorescens each @ 20 g/m2 at bimonthly intervals |
| 3. |
Planting density |
15 x 15 cm with 25 plants/m2 |
| 4. |
Planting stage and pinching level |
30 day old rooted cuttings and single pinching at the 5th node |
| 5. |
Precooling |
4oC for 4 hours |
| 6. |
Pulsing solution |
Sucrose 10 % + Citric acid 100 ppm + 8-Hydroxy Quinoline 400 ppm for 24 hours duration |
| 7. |
Holding solution |
Sucrose 5% + Citric acid 50 ppm + Benzyl Adenine 75 ppm |
| 8. |
Wrapping and packaging techniques |
Polyethylene sleeves 50 gauge thickness + CFB with 4 % vent |
* The precision production techniques are to be followed along with the cultural practices recommended for the conventional system.
Source:
1 . Standardization of precision production technologies for protected cultivation of Carnation - S.Karthikeyan
2
. http://www.flowers-cs.com/carnation.html
3
. http://arboretum.unl.edu/webimages/greatplants/dianthusprairiepink.jpg\
4
. http://botany.cs.tamu.edu/FLORA/dcs420/mi14/mi14024.jpg
|
|
























